Intelligent Agents in AI: Explained
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Intelligent agents are autonomous systems that perceive their environment and take rational actions to achieve goals.
- They are fundamental to AI, bridging decision-making capabilities and practical actions.
- Various types include simple reflex agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents.
- They operate through a Sense-Think-Act cycle, sometimes including a feedback loop for learning.
- Real-world applications span healthcare, finance, transportation, and customer service.
- While offering benefits like autonomy and efficiency, they present challenges such as complexity and ethical considerations.
Table of contents
- Intelligent Agents in AI: Explained
- Key Takeaways
- What are Intelligent Agents?
- The Deep Connection Between AI and Intelligent Agents
- Types of Intelligent Agents
- How Intelligent Agents Operate
- Real-World Applications
- Benefits and Challenges
- The Future of Intelligent Agents
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
- Frequently Asked Questions
Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as one of the most transformative forces in modern technology, revolutionizing everything from our smartphones to complex industrial systems. At the heart of this technological revolution lies a fundamental concept: intelligent agents. These autonomous entities form the backbone of AI systems, perceiving their environments and taking rational actions to achieve specific goals.
What are Intelligent Agents?
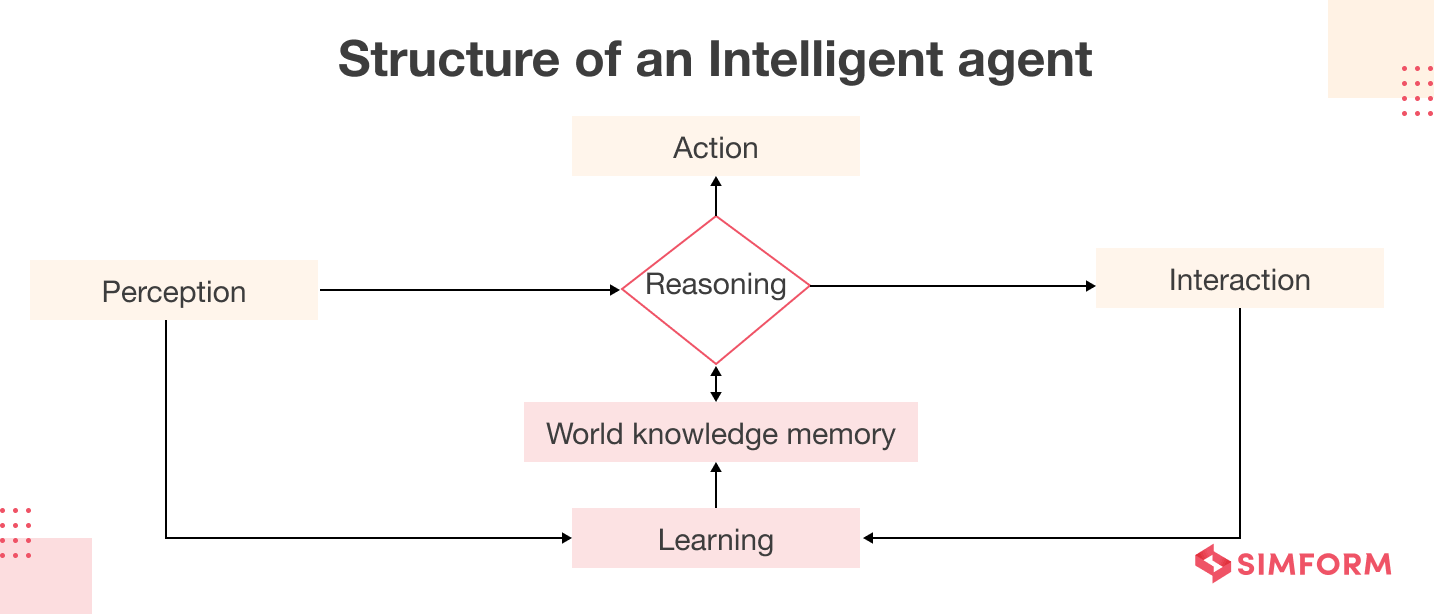
An intelligent agent is an autonomous system—whether software or hardware—that can perceive its environment, process information, and make decisions to achieve specific objectives. Think of it as a digital entity that can sense, think, and act on its own.
The core features that make an agent “intelligent” include:
- Perception – The ability to gather information from its environment
- Reasoning – Processing and analyzing information to make decisions
- Action – Taking steps that affect the environment
- Learning and Adaptation – The capability to improve performance over time
[Source: https://www.sapien.io/glossary/definition/intelligent-agent]
The Deep Connection Between AI and Intelligent Agents
Artificial intelligence and intelligent agents are intrinsically linked. In fact, AI is often defined as the science of designing and understanding intelligent agents. These agents serve as the bridge between abstract decision-making capabilities and practical actions in the real world. [Source]
Types of Intelligent Agents
Simple Reflex Agents
These are the most basic type of intelligent agents. They operate on simple if-then rules, responding directly to current inputs without maintaining any memory of past events.
Examples include:
- Basic thermostats
- Simple chatbots with pre-programmed responses
Goal-Based Agents
These agents make decisions based on specific objectives they aim to achieve. They consider the potential outcomes of their actions and choose paths that lead them closer to their goals.
Examples include:
- Navigation systems
- AI opponents in video games
Utility-Based Agents
These sophisticated agents make decisions by evaluating the desirability of different outcomes using a utility function.
Examples include:
- Product recommendation systems
- Financial trading bots
Learning Agents
The most advanced type, these agents can improve their performance over time through experience.
- Adaptive robotics
- Self-improving AI models [Source]
- Advanced customer service chatbots
[Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intelligent_agent]
How Intelligent Agents Operate
The operation of intelligent agents follows a systematic Sense-Think-Act cycle:
Sensing (Perception)
- Gathering data through sensors or input mechanisms
- Processing raw data into useful information
Reasoning (Decision-Making)
- Analyzing perceived information
- Using algorithms and models to make decisions
- Evaluating potential actions against goals or utility functions
Action
- Implementing decided actions
- Affecting the environment through outputs or physical movements
Feedback Loop (for Learning Agents)
- Evaluating action outcomes
- Adjusting future decision-making based on results
[Source: https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/ai-agents/]
Real-World Applications
Healthcare
- Diagnostic systems analyzing patient data
- Automated patient monitoring systems
- Personalized treatment planning tools
Finance
- Automated trading systems [Source]
- Risk assessment algorithms
- Fraud detection systems
Transportation
- Self-driving vehicle control systems
- Traffic management optimization
- Route planning systems
Customer Service
- Intelligent chatbots
- Virtual assistants [Source]
- Automated support systems
[Source: https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/ai-agents/]
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits
- Autonomy
- Reduced need for human oversight
- Continuous operation capability
- Consistent performance
- Efficiency
- Fast processing of complex tasks
- Reliable execution of repetitive operations
- Scalable performance
- Adaptability
- Performance improvement over time
- Adjustment to new conditions
- Learning from experience
Challenges
- Complexity
- Difficult design requirements
- Complex programming needs
- Resource-intensive operation
- Reliability
- Ensuring consistent performance
- Handling unexpected situations
- Maintaining accuracy
- Ethics and Control
- Balancing autonomy with oversight
- Addressing privacy concerns
- Managing job displacement issues
[Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intelligent_agent]
The Future of Intelligent Agents
Emerging Trends
- Enhanced Learning Capabilities
- Integration of advanced machine learning
- Improved adaptation mechanisms
- Better handling of complex scenarios
- Multi-Agent Systems [Source]
- Collaborative problem-solving
- Distributed intelligence
- Swarm robotics applications
- Ethical AI Development
- Transparent decision-making
- Fair and unbiased operations
- Responsible AI practices
Societal Impact
- Healthcare transformation through personalized medicine
- Smart city management and optimization
- Evolution of employment landscapes
- Development of new regulatory frameworks
Conclusion
Intelligent agents represent the cornerstone of modern artificial intelligence, enabling systems to perceive, reason, and act autonomously. Understanding these agents is crucial for anyone interested in AI’s current capabilities and future potential.
As technology continues to evolve, intelligent agents will become increasingly sophisticated and prevalent across industries. Their ability to learn, adapt, and make complex decisions will continue to transform how we live and work.
Additional Resources
For readers interested in diving deeper into intelligent agents, consider exploring these authoritative sources:
- Wikipedia: Intelligent Agent
- AWS: What are AI Agents?
- TechTarget: Intelligent Agent Definition
- Sapien AI Glossary: Intelligent Agent
Stay informed about the latest developments in AI and intelligent agents to better understand and prepare for the technological future ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is an intelligent agent in AI?
- An intelligent agent is an autonomous entity that perceives its environment and takes actions to achieve specific goals.
- How do intelligent agents learn?
- They learn by interacting with their environment and adjusting their actions based on feedback and outcomes.
- Where are intelligent agents used in real life?
- They are used in various sectors including healthcare, finance, transportation, and customer service.
- What are the challenges associated with intelligent agents?
- Challenges include complexity in design, ensuring reliability, and addressing ethical concerns.