Understanding Multi-Agent Systems and Their Strategic Implementation
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) provide scalable and robust solutions for complex problem-solving.
- Agents are autonomous entities capable of learning and adapting within their environment.
- Scaling MAS introduces challenges like increased complexity and resource demands, requiring strategic approaches.
- Implementing effective communication architectures is crucial for MAS success.
- Understanding MAS fundamentals aids in enhancing organizational AI capabilities.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Multi-Agent Systems and Their Strategic Implementation
- Key Takeaways
- What Are Agents and Multi-Agent Systems?
- Understanding Agents
- Multi-Agent Systems Defined
- Key Characteristics of MAS
- Types of Agents in MAS
- Real-World Applications
- The Complexity of Scaling Multi-Agent Systems
- Technical Challenges
- Communication Management Architectures
- Strategies to Mitigate Scaling Issues
- Strategies for Implementing Multi-Agent Systems
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, artificial intelligence (AI) is driving unprecedented transformation across industries. At the forefront of this revolution are multi-agent systems (MAS), offering scalable, adaptive, and robust automation solutions that are reshaping how organizations operate and compete.
Multi-agent systems have emerged as a crucial technology for organizations seeking to solve complex problems and gain a competitive edge. These systems enable businesses to handle tasks that would be impossible for single-agent solutions, offering a distributed approach to problem-solving that scales with organizational needs.
This comprehensive guide will explore the fundamentals of agents and multi-agent systems, examine the complexities involved in scaling MAS, and provide strategic insights for implementation. Whether you’re investigating MAS for your organization or seeking to expand your existing AI capabilities, this post will equip you with essential knowledge for success.
What Are Agents and Multi-Agent Systems?
Understanding Agents
An agent in the context of AI is a system or software entity that operates autonomously to perform specific tasks. These agents interact with their environment, process information, and often possess the ability to learn and adapt based on their experiences.
Multi-Agent Systems Defined
A multi-agent system comprises multiple agents operating within a shared environment. These agents collaborate or coordinate their actions to achieve objectives that would be difficult or impossible for a single agent to accomplish alone.
Key Characteristics of MAS
- Distributed Intelligence: Multiple agents contribute their capabilities to solve complex problems.
- Parallel Problem-Solving: Agents work simultaneously on different aspects of tasks.
- Specialization: Each agent can be optimized for specific functions.
Types of Agents in MAS
Multi-agent systems can include various types of agents:
- Software programs
- Robots
- Human teams acting as agents
Real-World Applications
1. Autonomous Vehicle Fleets:
- Vehicles communicate with each other and traffic infrastructure.
- Optimize routes and reduce congestion.
- Enhance safety through coordinated movements.
2. Manufacturing Robotics:
- Coordinated teams of robots work on assembly lines.
- Increase efficiency and precision.
- Adapt to production changes in real-time.
3. Financial Trading:
- Multiple specialized bots analyze market data.
- Execute coordinated trading strategies.
- Maximize profits through distributed decision-making.
Sources: IBM Think Blog on Multi-Agent Systems, Wikipedia: Multi-Agent System, Smythos: Examples of Multi-Agent Systems
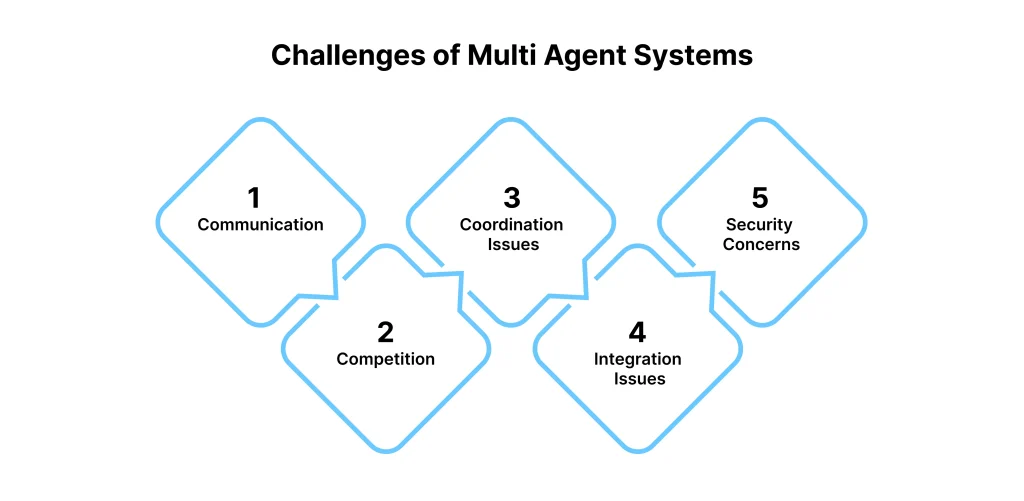
The Complexity of Scaling Multi-Agent Systems
Technical Challenges
Increased Complexity
- Growing number of agent interactions.
- More complex coordination requirements.
- Challenging dependency management.
Resource Demands
- Higher computational requirements.
- Increased network infrastructure needs.
- Enhanced storage and processing capabilities.
Interoperability Issues
- Need for standardized communication protocols.
- Robust middleware requirements.
- Integration challenges with existing systems.
Communication Management Architectures
1. Network Architecture
- Peer-to-peer communication.
- Decentralized control.
- Direct agent interactions.
2. Supervisor Architecture
- Central agent oversight.
- Coordinated decision-making.
- Hierarchical control structure.
3. Hybrid Architectures
- Combined approaches.
- Flexible implementation.
- Task-specific optimization.
Strategies to Mitigate Scaling Issues
1. Modular Design
- Clear agent role definition.
- Well-defined interfaces.
- Simplified interactions.
2. Middleware Investment
- Robust communication management.
- Resource sharing optimization.
- Coordination facilitation.
3. Architecture Reviews
- Regular system assessment.
- Scalability planning.
- Proactive problem resolution.
Sources: LangChain AI – Multi-Agent Concepts, Wikipedia: Multi-Agent System
Strategies for Implementing Multi-Agent Systems
Implementing MAS requires careful planning and strategic execution. Here are some best practices:
1. Start with a Clear Vision
- Define objectives and desired outcomes.
- Identify problems that MAS can solve effectively.
- Ensure alignment with organizational goals.
2. Invest in Training and Development
- Upskill your team on MAS technologies.
- Promote a culture of continuous learning.
- Encourage collaboration between departments.
3. Pilot Projects and Scaling
- Begin with small-scale pilot projects.
- Test and refine MAS implementations.
- Gradually scale successful projects organization-wide.
Conclusion
Multi-agent systems represent a significant advancement in artificial intelligence, offering powerful solutions for complex, large-scale problems. By understanding the fundamentals of MAS and strategically planning their implementation, organizations can harness these technologies to gain a competitive advantage and drive innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a multi-agent system in AI?
A multi-agent system in AI is a collection of autonomous agents that work together within an environment to solve problems that are beyond the capabilities of individual agents.
Why are multi-agent systems important for businesses?
They enable businesses to tackle complex tasks through distributed problem-solving, enhancing efficiency, scalability, and adaptability in operations.
What are the challenges in implementing MAS?
Challenges include technical complexities, resource demands, interoperability issues, and the need for effective communication architectures.
How can organizations mitigate scaling issues in MAS?
By adopting modular designs, investing in robust middleware, and conducting regular architecture reviews to ensure scalability and performance.
What are some real-world applications of MAS?
Applications include autonomous vehicle fleets, manufacturing robotics, and financial trading systems where coordination and collaboration are essential.